China, generally considered as a homeland of the tea plant and tea culture, is one of the most important tea cultivators and producers. Local tea gardens spread across an area extending 1.000.000 hectares, bordered by 90°of eastern longitude and 18°and 37°northern latitude, that is traditionally divided into four basic regions.
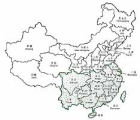
The south-western region includes Yunnan (Jün-nan), Guizhou (Kuj-čchou) and Sichuan (S´-čchuan) provinces. Climatic conditions are not uniform thanks to the complicated topography of this area, but the predominant climate is pluvial subtropical, really convenient for tea leaves growth. Most of the local plantations are situated at the higher altitudes.
The region of southern China is made up of Guangdong (Kuang-tung), Guangxi (Kunang-si), Fujian (Fu-ien), Taiwan (Tchajwan) and Hainan (Chaj-nan) provinces. With the exception of the northernmost situated areas of the region, the local climatic and soil conditions for tea plant cultivation are almost ideal here. The average yearly temperature is about 20°C and it doesn´t drop under 7°C, even in Winter, precipitation amount ranges between 1.200 and 2.000 millimeters. The tea leaves are harvested more than ten months a year, a short dormancy period takes place only in the coldest winter months.
The region south of the Jang-c´River is made by the Zhejiang (Če-?iang), Hunan (Cunan), Jiangxi (?iang-si) provinces and the southern part of the Anhui (An-chuej), Jiangsu (?Iang-su) and Hubei (Chu-pei) provinces. Local plantations are situated in mountain and partly also in high-mountain areas. The climate is mild with the average yearly temperature about 16°C, but Winters are quite cold
(-8°C). Yearly precipitation amount ranges between 1.400 and 1.600 m, while up to 80% of rainfalls occur in Spring and in the beginning of Summer. Autumn, contrarily, represents the drought season.
The region located north of the Jang-c´ River is made up of the Henan (Che-nan), Shaanxi (Šan-si), Gansu (Kan-su), Shandong (Šan-tung) provinces and the northern area of Anhui (An-chuej), Jiangsu (?iang-su) and Hubei (Chu-pej) provinces. Climatic conditions for tea plant cultivation are not really convenient, although the average yearly temperature is about 15°C, but Winters are quite cold with temperatures dropping bellow -10°C and the climate is rather dry, with total precipitation amount below 1.000 m. High-quality tea is grown then only in high-mountain areas with favourable local micro-climates.
China produces probably all possible types of tea, green, half-green, black (labeled traditionally as red), white, dark and yellow tea, also pressed, aromatized and other special types of tea.
Yunnan is situated on the Yunnan Guizhou plateau and tea is cultivated here mainly in the southern regions (Si-šuang-pan-na and Simao Prefecture), to some extent also in the western and north-western part of the Province. It produces red, green and dark tea (green as well as red variety). The most famous floricultural region is Menghai, producing the highest grades of red tea and also famous dark tea called Pu Erh.
Guizhou is situated near the eastern border of Yunnan. It produces red, half-green and to some extent also green and dark tea. Plantations are located practically all over the province, with the exception of its central part.
Sichuan is situated northward of Yunnan and Guizhou and the tea plant is cultivated all over the province territory. It produces red, green, half-green and dark (pressed) tea.
Guangxi is situated eastward of Yunnan and south-eastward of Guizhou. It produces mainly green, to a lesser extent also red and dark pressed tea. An important part of the local production is made by aromatized teas.
Guangdong is situated eastward of Guangxi and the most important floricultural regions are located in the South and East of the province. It produces red, green and half-green tea.
Hainan is an island in South China Sea, situated southward of Guangxi. Local climate is specific, subtropical with high enough humidity, hence ideal for tea leaves growth. It produces red, green and half-green tea. The most important production region is the Wuzhi Shan Mountains region.

Fujian is situated north-eastward of Guangdong and its most important tea regions are located near the eastern border of the province and also on the cost of the Taiwan Gulf. It produces green, half-green, red and white tea, some local teas are used as the base material for aromatized teas. The most important floricultural regions are Anxi, the homeland of famous half-green tea Tie Guanyin, and Wuyi Mountains, well-known for its first-grade green and half-green teas.
Taiwan is an island province situated in the East China Sea, eastward from Guangdong and Fujian. The most important production regions are located in the central part of the island. They produce half-green, green, red and aromatized teas. The most famous production area is the Tung Ting Mountain, home of the most famous variety of the fabled half-green tea Dung Ti.
Zhejiang is situated northward of Fujian and Zhejiang. Tea plant is cultivated here almost evenly on the whole territory of the province. It produces mainly green and half-green tea, to a lesser extent also red and aromatized tea.
Jiangsu is situated northward of Zhejiang and eastward of Anhuie. The most important floricultural regions are situated in the South and in the central areas of the province. They produce mainly green, to a lesser extent also red and aromatized tea.
Anhui is located westward of Jiangsu and northward of Jainxi. The most important floricultural regions are situated in the South-west and in the central parts of the province. They produce green, red and aromatized tea. The most important gardens are situated in the Huangshan Mountains (Yellow Mountains), the homeland of famous Huangshan Mao Feng, and in Qimen region, the homeland of the worldwide famous tea of the same name.
Hubei is located westward of Anhui and northward of Hunan. The tea plant is cultivated, with the exception of the eastern industrial part, on the whole territory of the province. The production consists of red, green, aromatized and to a lesser extent also dark tea.
Shangdong is situated northward of Jiangsu and it is the northernmost tea producing territory of China. Tea plant is cultivated in the South and southeast of the province, which produces exclusively green tea.
Henan is situated northward of Anhui. The ta plant is cultivated here only in the southernmost parts of the province, which produces exclusively green tea.
Shaanxi is situated westwards of Henan and north-eastward of Sichuan. The tea plant is cultivated here only in the southernmost parts of the province, which produce exclusively green tea.
Gansu is located westward of Shaanxi and Northward of Sichuan. The tea plant is cultivated only in the south-western foreland of the province and produces exclusively green tea.